The Fall of Silicon Valley Bank and the Fourth Industrial Revolution
Silicon Valley Bank (SIVB), a renowned financial institution, has become the second-largest bank failure in US history, posing those in the media to question the risks of contagion in the banking sector (news article). SIVB and Silvergate Bank (SI) were popular among start-ups, which are facing cash outflows due to high-interest rates, inflation, and increased regulatory costs. This is leading to higher withdrawals, lower deposits, and banks being forced to sell bonds on their books at a loss. The bonds, mainly US Treasury securities, were undervalued due to the high-interest rate but would have redeemed at full value upon maturity otherwise. While this does not hold true for other banks that have more diversified depositors, it remains to be seen if the current situation may hamper the Federal Reserve's ability to increase interest rates, leading to prolonged inflationary pressure. My expectation is we will see the Federal Reserve walk back their rhetoric for higher interest rates so they can assess the vulnerabilities in smaller, regional banks. This of course means accepting the reality of a higher for longer inflation rate.
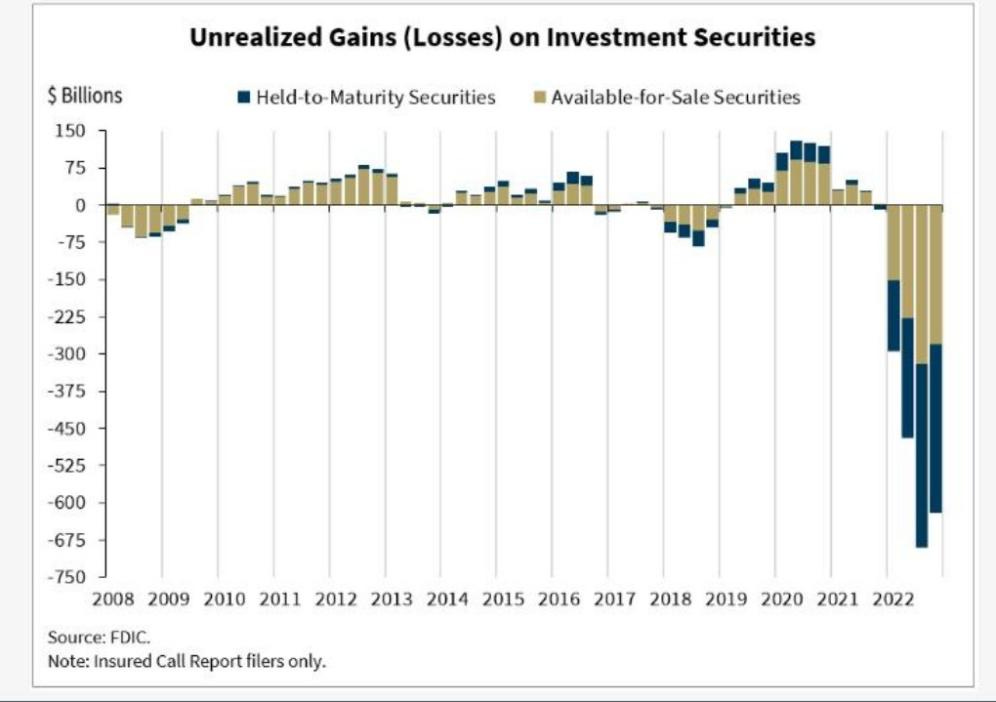
(FDIC Chairman Martin Gruenberg remarks: "The current interest rate environment has had dramatic effects on the profitability and risk profile of banks’ funding and investment strategies. First, as a result of the higher interest rates, longer term maturity assets acquired by banks when interest rates were lower are now worth less than their face values. The result is that most banks have some amount of unrealized losses on securities. The total of these unrealized losses, including securities that are available for sale or held to maturity, was about $620 billion at yearend 2022. Unrealized losses on securities have meaningfully reduced the reported equity capital of the banking industry." (link)
From a historical perspective, The Second Industrial Revolution, which took place from the late 19th century to the early 20th century, was a time of significant technological advancement, marked by the widespread adoption of electricity, the telephone, and the internal combustion engine. During this period, there were instances of bank failures in the United States due to various factors such as fraud, financial panics, and economic downturns. One of the most notable failures was the Panic of 1893, which resulted in the failure of numerous banks and financial institutions. However, it's worth noting that bank failures during the Second Industrial Revolution were not directly caused by technological advancements but rather by economic and financial factors that have always affected the banking industry. During that time, the following companies became household names:
General Electric (GE): Founded in 1892, GE is one of the largest and most diversified companies in the world, involved in industries ranging from aviation to healthcare. An investment in GE during its early days would have yielded significant returns over time.
Ford Motor Company (F): Founded in 1903, the company revolutionized the automobile industry with the introduction of the assembly line, and it quickly became one of the most successful companies in the world.
IBM (IBM): Founded in 1911, IBM was originally involved in the production of tabulating machines and other computing equipment. Over time, it has become one of the largest and most successful technology companies in the world.
Coca-Cola (KO): Founded in 1892, Coca-Cola has become one of the most recognizable and successful brands in the world, producing a range of beverages that are sold in virtually every country on the planet.
Procter & Gamble (PG): Founded in 1837, P&G is a multinational consumer goods company that produces a range of popular brands such as Tide, Pampers, and Gillette.
Today, the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) is bringing about a paradigm shift in how we live and work, integrating digital technologies and physical systems. 4IR leverages the foundation of mechanization, mass production, and automation to integrate artificial intelligence, internet of things (IoT), robotics, biotechnology, and advanced materials. It is transforming industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, and energy. Robotics and automation are making manufacturing more efficient, flexible, and customizable, while digital technologies are enabling personalized medicine and telemedicine in healthcare. Connected and autonomous vehicles are revolutionizing transportation, and in energy, nuclear power, natural gas, and renewable sources such as solar and wind power are becoming more cost-effective and adopted.
From an investment management perspective, this necessitates managing risks such as high-interest rates, inflation, black swan events, market and political risks, Federal Reserve action errors, and debt ceiling debates. Investors can capitalize on the opportunities presented by companies at the forefront of 4IR, offering a great chance to beat inflation. Some viable investment options include Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) such as XSD for exposure to the semiconductor industry, and XLE and VDE for energy-related investments. Also, software companies such as Microsoft (MSFT), Shopify (SHOP), and Unity (U) offer promising opportunities for investors looking to leverage 4IR.
For Cash management solutions such as FDIC insurance covering up to $250,000 in checking and savings accounts is the MaxMyInterest platform.
Here are some interesting AI tools:
Image Generation:
https://stablediffusionweb.com/#demo
https://deepdreamgenerator.com/
https://www.midjourney.com/app/
Others:
Disclaimer. This post is for general information purposes only. It does not constitute investment advice or a recommendation or solicitation to buy or sell any investment and should not be used in the evaluation of the merits of making any investment decision. It should not be relied upon for accounting, legal or tax advice or investment recommendations.